Industry 4.0: The new revolution

Industry 4.0 or intelligent industry is a term that is intrinsically linked to the digital transformation of companies, especially in the industrial sector. By integrating disruptive technologies such as Big Data, Cloud Computing, Augmented Reality and Artificial Intelligence in production models and manufacturing systems, the aim is to create intelligent factories and companies capable of generating smart grids or smart distribution networks.
However, the concept of industry 4.0 should not be confused with that of the fourth industrial revolution. The main reason is that the former can be considered the most tangible product of a new revolution in the making and that will bring with it other technological advances, in addition to intelligent and connected machines and systems. Nanotechnology, genetic sequencing and quantum computing are just a small example of the scope of this fourth industrial revolution which, unlike previous revolutions, is characterized by the fusion and interaction between technologies.
If you want to know more about industry 4.0 and how we have evolved from the first to the fourth industrial revolution, keep reading the article in which we reveal everything you need to know about this unstoppable phenomenon.
The beginnings of industry 4.0
The concept of industry 4.0 is a term that emerged in 2011 during the celebration of the Hannover Messe technology fair (Germany) and that was subsequently reflected in the report Recommendations for implementing the strategic initiative industry 4.0 (German Academy of Sciences and Engineering). DFKI (German Center for Research in Artificial Intelligence), academic institutions, public bodies and leading German companies all collaborated to create this document. The Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology, the Federal Association for Information Technologies, Telecommunications and New Media (BITKOM), Hewlett-Packard GmbH, Siemens AG, Bosch Software Innovations GmbH and Telekom AG are just a small sample of the many companies that participated in the preparation of the report.
The document talks about the future of industry 4.0, new opportunities and future business models. It also gives different examples of the application of technologies related to intelligent industry. Technologies whose benefits include increased efficiency and productivity, through the creation of fully integrated, automated and optimized production flows.
In relation to the concept of industry 4.0, the report explains that “In essence, Industrie 4.0 will involve the technical integration of CPS into manufacturing and logistics and the use of the Internet of Things and Services in industrial processes.” In addition, it underlines that “This will have implications for value creation, business models, downstream services and work organization”.
CPS (cyber-physical systems), can be defined as any device that integrates computing, storage and communication capabilities to control and interact with a physical process. Normally, CPS are connected to each other and to other storage and data management services. A few years ago, even though machines generated data, they were isolated. Now there are an ever-increasing number of devices connected to different types of networks that produce information and use it to interact with other machines. An example of a cyber-physical system is autonomous cars, which, within an intelligent transport network, can communicate with each other, the road infrastructure they circulate on, the road control centers and the occupants of the vehicle, to determine, for example, the best route. Furthermore, all the interaction is done in real time.
In the manufacturing environment, CPS comprises intelligent machines, systems and production facilities capable of autonomously exchanging information with each other, monitoring processes, executing actions and controlling each other independently. This results in improvements in industrial processes, from manufacturing, use of materials, supply chain management to the entire product life cycle. Smart factories arguably employ a completely new approach to production. Smart products are identifiable and locatable at all times, through real-time information. Manufacturing systems are vertically networked with business processes in companies and factories; and horizontally with dispersed value networks that can be managed in real time, for example, from the moment an order is placed to distribution logistics. Furthermore, the flexibility that characterizes this new industrial model enables last-minute changes in production and provides an agile and rapid response capacity, in the event of possible supplier errors or changes in customer needs. A new industrial environment in which, thanks to intelligent assistance systems, can automate routine and repetitive tasks while freeing human workers to focus on performing tasks that truly add value to the company.
For all these reasons, we could say that industry 4.0 is a concept that describes the digitization of industrial systems and processes, and their interconnection through the Internet of Things (IoT) and Internet of Services (IoS) to achieve greater flexibility and independence in production processes. Thus, industry 4.0 constitutes a development framework for the design, implementation and management of complex business ecosystems, which provide information in real time and enable autonomous interactions between machines, systems and objects.
The concept of intelligent industry has been taking shape over the last few years, with the annual celebration of the Hanover Messe fair as a reference framework. In 2016, they presented the Industry 4.0 Standardization Committee to promote international standards. A year later, they proposed the intelligent industry or “intelligent factory 4.0: the combination of automation, digital twins, Cobots and AI”. During the 2018 event and under the motto “Integrated industry – Connect and collaborate”, digitalization was discussed as a critical success factor in the logistics sector and the manufacturing industry; and, the power of digital integration as a key factor to achieving maximum business performance. In successive years, the German trade fair, which is considered the most important global platform for all technologies related to industrial transformation, has addressed relevant issues such as the potential of AI and robotics in industry, the changes resulting from the new 5G mobile communications standard for industrial applications, green energy and hydrogen, and the multiple applications of industry 4.0 technologies in the fight against climate change.
How did we get to industry 4.0?
To understand this shift in the industrial economy, it is worth reviewing the changes that industry, companies, and society have experienced over the last centuries. So, we will take a look at the different industrial revolutions that have marked the history of humanity.
The first industrial revolution that took place during the 18th and 19th centuries involved a complete transformation of work systems and social structure. It went from an economy based on agriculture, livestock, and crafts to one based on industrial production and mechanization. It could be said that the first industrial revolution marked the beginning of the first industries, thanks to the steam engine and the invention of the railway.
The second industrial revolution began during the second decade of the 19th century and lasted until the middle of the 20th century. A period marked by mass production, the assembly line, and the emergence of large companies. In addition, this second industrial revolution was characterized by using new materials such as stainless steel and aluminum; the creation of chemicals such as fertilizers and explosives; the use of new energy sources such as electricity and oil; new methods of transportation, such as gasoline cars or the electric railway; and, also, the invention of the telegraph, the telephone, and the cinematograph.
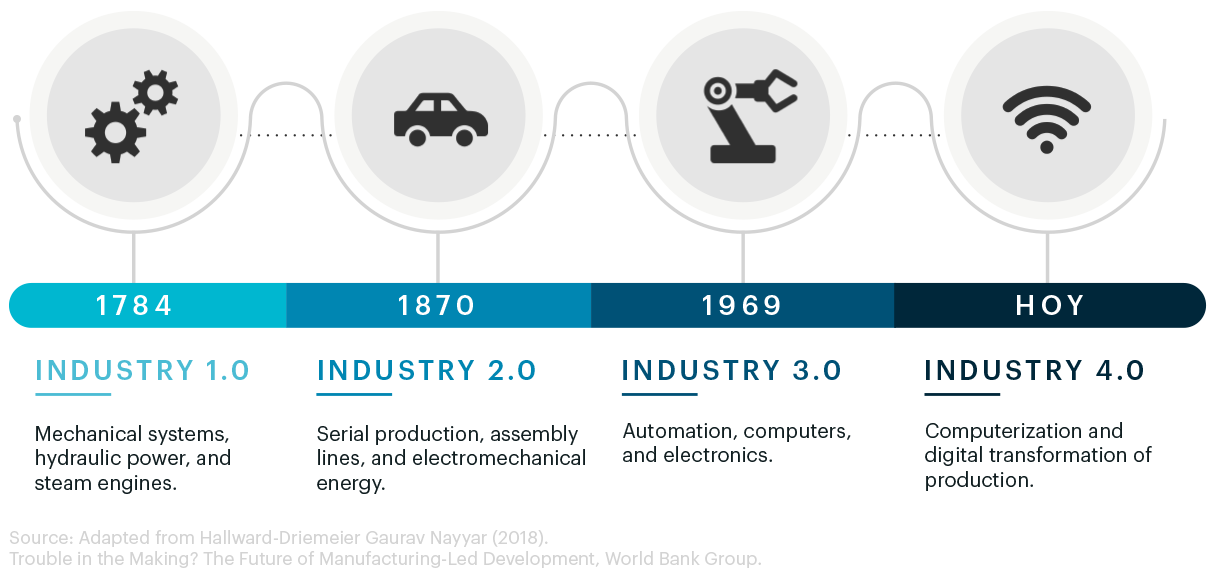
The third industrial revolution began in the mid-20th century and is marked by the deployment of electronics, computing, and Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). The widespread use of the Internet, personal computers and mobile phones, automated production, biotechnology, and the development of renewable energies are clear examples of the progress of this revolution, as well as the development of the information and knowledge society.
Finally, the concept of the fourth industrial revolution was coined by Klaus Schwab, a German economist and businessman who founded the World Economic Forum, first in a 2015 article published by Foreign Affairs, “Mastering the Fourth Industrial Revolution”; and, later, in 2016 in his homonymous work. With this term, the author refers to a stage in which “physical and virtual manufacturing systems cooperate with each other in a flexible way and at a global level”. The foundations on which this new Industrial Revolution is built are IoT, robotics, connected devices, cyber-physical systems, and industry 4.0. As Schwab explains in his book, the three main reasons that show that we are witnessing a fourth industrial revolution are:
Speed: The fourth industrial revolution is characterized by its exponential rather than linear evolution. A quality that makes it different from the previous ones. The author explains the main reasons for this change to be the interconnected world and the continuous technological advances such as AI, quantum computing, 3D printing, and Blockchain.
Breadth and depth: The combination of multiple technologies is causing changes that affect not only the economy and companies but also society and the very identity of individuals.
Impact on systems: The advances and technological characteristics of this new stage are so sophisticated that they are changing the core systems in countries, companies, industries, and society as a whole.
Everything seems to indicate that we are witnessing a new change of course not only in industry but also at an economic and social level with the advent of what Schwab and other global leaders have named the “Great Reset” of the planet. An initiative that was unveiled at the World Economic Forum 2021 aiming to build a more sustainable and equitable system in which the new technologies linked to the fourth industrial revolution are used, including those associated with industry 4.0. The initiative is to use technology as an instrument of harmonization rather than polarization, and that favors a greener and more intelligent development.



